Fault Detection; Isolation; Identification, and Recovery (FDIIR) systems are essential for increasing the reliability of lidar sensors. Knowing the influence of different faults on lidar data is the first crucial step towards fault detection for lidar sensors in automated vehicles. Therefore, a team at the Austrian University of Graz investigated the influences of sensor cover contaminations on the output data of the lidar point cloud. The pictures show the experimental set-up and the different types of cover contaminations applied in the experiments. Such experiments simulate that a lidar sensor is not directly exposed to the vehicle exterior but sheltered by a cover (much like a headlamp).
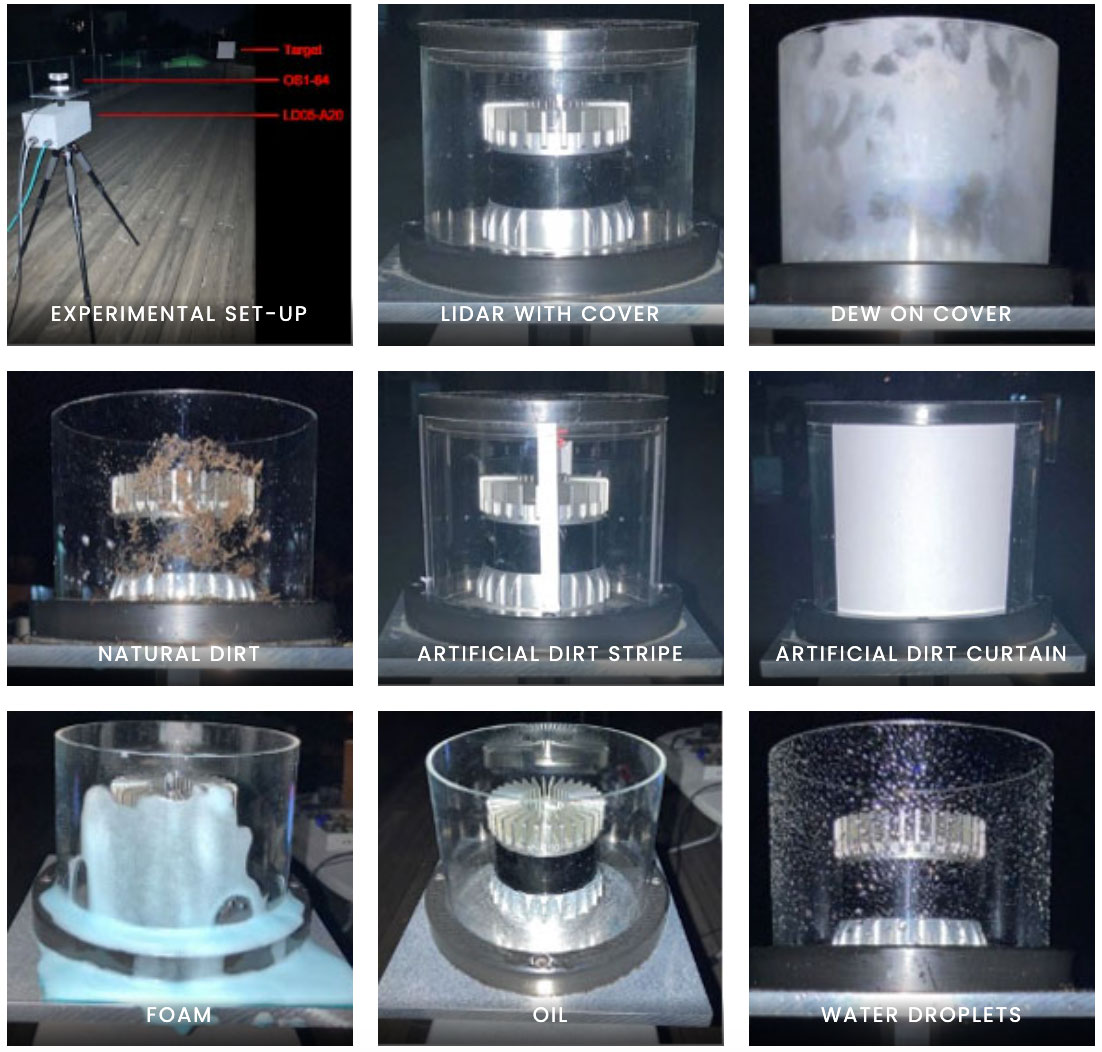
For evaluation, the team recorded the point clouds generated by the lidar sensor under the different conditions. As a figure of merit they used the number of reflections on target during a predefined time interval ( see example in diagram ).
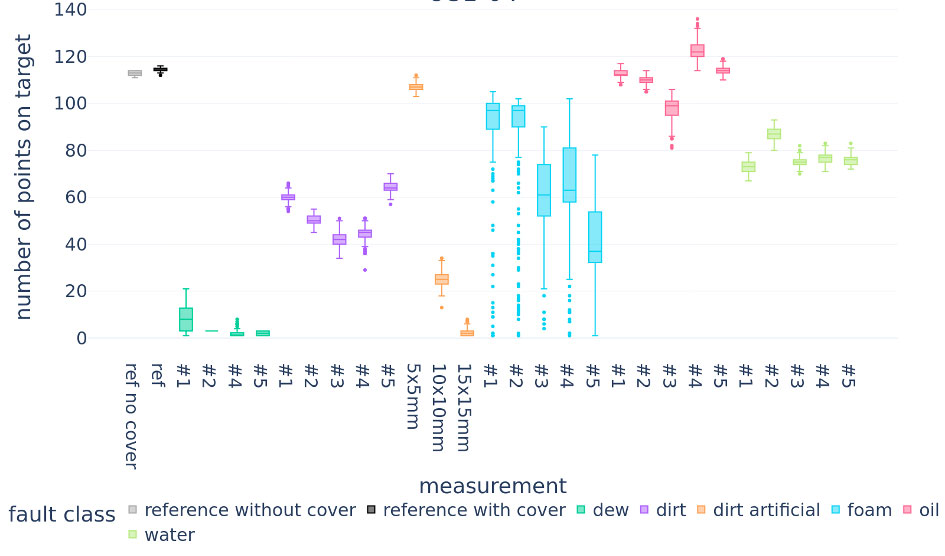
The reference measurements without contamination revealed a target of 110 points. For the different contamination types, five measurements were conducted to show some statistical relevance. Unsurprisingly, dew; artificial dirt over the entire transmitter, and foam lead to severe faults—sometimes even complete sensor blindness.
The team plan to investigate other contamination types like ice; salt water; salt residue, and accumulated snow on the sensor cover. Future work may also investigate the dependency of the results on target distance and material.
The researchers suggest that fault injection should be standardised to compare the lidar offerings from different manufacturers in terms of performance reduction by various kinds of contamination.
DVN comment
Like in a number of other publications, lidar sensor disturbance by environmental influences gets an increasing amount of attention. For a good understanding of lidar sensor reliability such investigations should finally lead to standardised test program. In a next and much broader step this research should not only include lidar sensors, but has to be extended to the reliability of fused sensors within the sensor suite of camera; radar, and lidar.
